
- ALLOW FILEZILLA FTP UBUNTU SERVER PASSWORD
- ALLOW FILEZILLA FTP UBUNTU SERVER DOWNLOAD
- ALLOW FILEZILLA FTP UBUNTU SERVER MAC
number of clients and connections per IP for local users can be limited by adding the information in /etc/nf: The file specified by userlist_file will now contain users that are able to login. If you only want to allow certain users to login, add the line: Userlist_file now specifies the file which lists users that are not able to login. It is possible to prevent users from logging into the FTP server by adding two lines to /etc/nf: In this case, the file specified by chroot_list_file lists users that are not in a chroot jail. This will make local users jailed by default. The chroot_list_file variable specifies the file which contains users that are jailed.įor a more restricted environment, specify the line: To enable this, add the following lines to /etc/nf: # Directory to be used for an anonymous loginĪnon_root=/example/directory/ Chroot jailĪ chroot environment that prevents the user from leaving its home directory can be set up. # Maximum transfer rate for an anonymous client in Bytes/second
ALLOW FILEZILLA FTP UBUNTU SERVER PASSWORD
etc/nf # No password is required for an anonymous login the following options (see nf(5) for more): # Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create # obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user. # has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. # Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. # Allow anonymous FTP? (Beware - allowed by default if you comment this out).
ALLOW FILEZILLA FTP UBUNTU SERVER DOWNLOAD
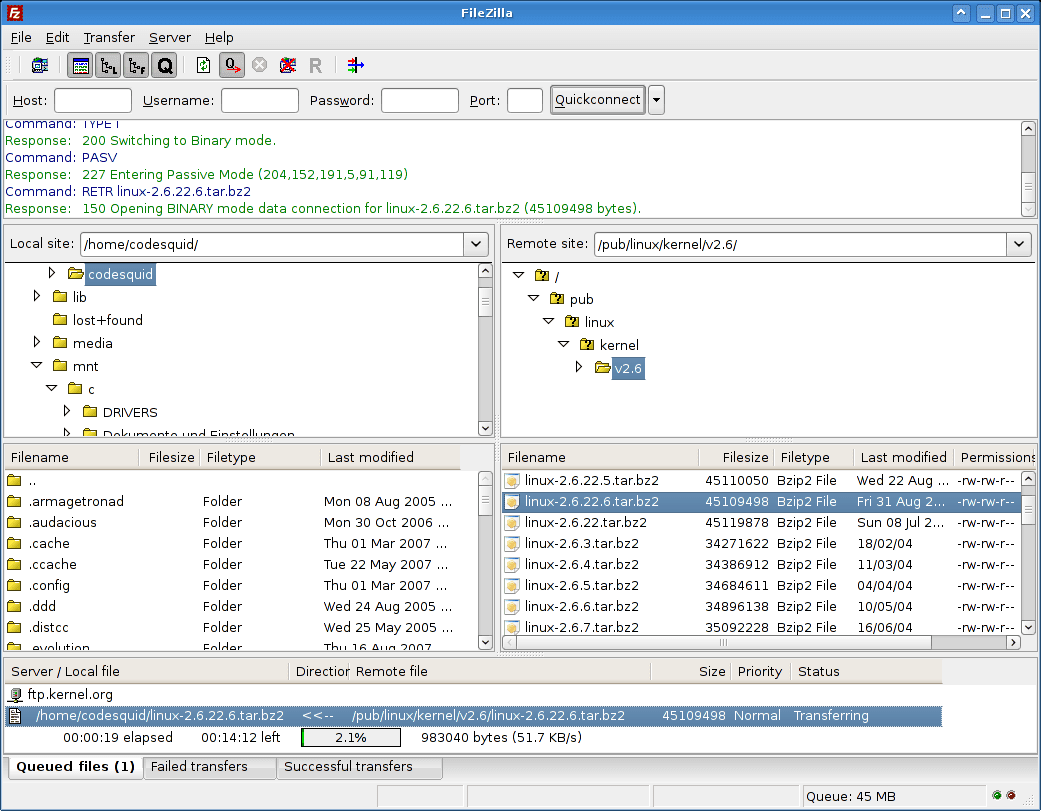
By default, anonymous logins are enabled for download only from /srv/ftp: These lines controls whether anonymous users can login. One must set the line local_enable in /etc/nf to YES in order to allow users in /etc/passwd to login: The WRITE_ENABLE flag must be set to YES in /etc/nf in order to allow changes to the filesystem, such as uploading: Better to configure firewall rules to limit access. libwrap/tcp-wrappers is not dependency of vsftpd and not installed by default. Once the file is successfully transferred, you should be able to see it in action.Reason: I believe this information is deprecated. If you’re using a command-line FTP client, you can use the FTP PUT command. If you’re using a graphical FTP client, you can usually drag and drop the file from one directory to the other. Transfer the file from your home directory to the server using normal FTP transfer conventions.Your FTP client should now connect to the server and enter the /opt/lampp/htdocs/ directory, which is the default Web server document root.

System, use the network hostname or IP address of the XAMPP server.Įnter your Linux username and password as your FTP credentials. If you’re connecting to the server from the same system, use Start an FTP client like winSCP or FileZilla and enter connection details as below.You can now transfer files to the XAMPP server using the steps below: Ensure that proFTPD is running in the XAMPP control panel.Change the ownership and permissions of the htdocs/ subdirectory of the XAMPP installation directory (typically, /opt/lampp) so that it is writable by the the new ftp group.
Add your account (in this example, susan) to the new group.This group will contain those user accounts allowed to upload files via FTP. Open a new Linux terminal and ensure you are logged in as root.Ĭreate a new group named ftp. Make sure to start the service from XAMPP control panel -> manage servers.įurther complete instructions can be found at localhost XAMPP dashboard -> How-to guides -> Configure FTP Access.
ALLOW FILEZILLA FTP UBUNTU SERVER MAC
XAMPP for linux and mac comes with ProFTPD.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
